How to Disable Antimalware Service Executable on Win 11/10?
If you have opened Task Manager and noticed Antimalware Service Executable consuming high CPU, memory, or disk usage, you are not alone. This process is part of Microsoft Defender Antivirus, the built-in security program in both Windows 11 and Windows 10. The service runs in the background to protect your system from viruses, malware, ransomware, and other threats.
The actual file behind Antimalware Service Executable is called MsMpEng.exe. It performs real-time protection, background scanning, and automatic updates of virus definitions. While this protection is essential, some users experience performance slowdowns, especially on low-end PCs.
Let us know the methods and steps in detail!
How to Disable Antimalware Service Executable on Windows 11/10?
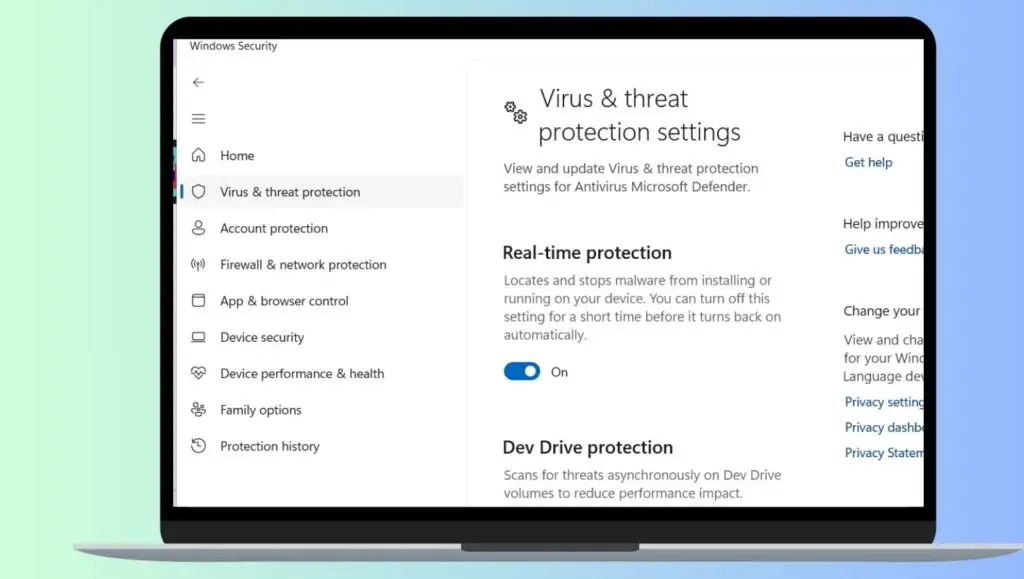
To disable Antimalware Service Executable on Windows 11 or Windows 10, follow these steps:
- Open Windows Security from the Start menu.
- Click Virus and threat protection.
- Select Manage settings under Virus and threat protection settings.
- Turn off real-time protection.
To disable it permanently, you must use the Group Policy Editor or install a third-party antivirus.
Now, let us go deeper and understand each method step by step.
Before making changes, it is important to understand that real-time protection automatically turns back on after restarting your PC. The following method temporarily stops the service.
Step 1: Open Windows Security
Click the Start menu and type Windows Security. Press Enter to open it. You can also open it through Settings by pressing Windows key + I, then selecting Privacy and Security, and clicking Windows Security.
This application controls all Microsoft Defender Antivirus features, including firewall, virus scanning, and device protection.
Step 2: Go to Virus and Threat Protection
Inside Windows Security, click on Virus and threat protection. This section manages real-time protection, scan options, and threat history.
You will see your current protection status displayed at the top of the window.
Step 3: Open Manage Settings
Scroll down until you find Virus and threat protection settings. Under this section, click on Manage settings.
This page allows you to enable or disable real-time scanning, cloud-delivered protection, automatic sample submission, and tamper protection.
Step 4: Turn Off Real-Time Protection
Toggle off Real-time protection.
You may see a User Account Control prompt asking for permission. Click Yes to confirm.
Once disabled, the Antimalware Service Executable process will reduce its CPU and disk activity significantly. However, Windows will warn you that your device is vulnerable.
Step 5: Disable Cloud Delivered Protection and Automatic Sample Submission
To further reduce background activity, turn off Cloud-delivered protection and Automatic sample submission.
These features communicate with Microsoft servers to detect new threats, which can occasionally cause network or CPU usage spikes.
Keep in mind that these settings may re-enable automatically after restarting your computer.
Alternative Method Using Task Scheduler
Another way to reduce Antimalware Service Executable activity is by adjusting scheduled scans.
Step 1: Open Task Scheduler
Press Windows key + R, type taskschd.msc, and press Enter.
Step 2: Navigate to the Microsoft Defender Folder
In the left panel, go to Task Scheduler Library, then Microsoft, then Windows, and finally select Windows Defender.
Step 3: Disable Scheduled Scans
Right-click on Windows Defender Scheduled Scan and select Disable.
This prevents automatic background scans that can cause high disk usage.
Note that real-time protection will still function unless disabled separately.
How to Disable Permanently?
If you want to permanently disable Antimalware Service Executable, you must use either Group Policy Editor, Registry Editor, or install a third-party antivirus program. When another antivirus is installed, Microsoft Defender automatically disables itself.
This method works only in Windows Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions.
Method 1: Using Group Policy Editor
Step 1: Open Group Policy Editor
Press Windows key + R, type gpedit.msc, and press Enter.
This opens the Local Group Policy Editor.
Step 2: Navigate to Microsoft Defender Settings
Go to Computer Configuration, then Administrative Templates, then Windows Components, and select Microsoft Defender Antivirus.
Step 3: Turn Off Microsoft Defender Antivirus
- Double-click on Turn off Microsoft Defender Antivirus.
- Select Enabled and click Apply, then OK.
- Restart your computer.
After restarting, the Antimalware Service Executable will no longer run in the background.
Method 2: Disable Using Registry Editor
This method is suitable for Windows Home users where the Group Policy Editor is unavailable.
Step 1: Open Registry Editor
Press Windows key + R, type regedit, and press Enter.
Click Yes when prompted.
Step 2: Navigate to Defender Key
Go to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender
If the Windows Defender key does not exist, right-click Microsoft, choose New, then Key, and name it Windows Defender.
Step 3: Create a New DWORD Value
- Right-click in the right panel, select New, then DWORD 32 bit Value.
- Name it DisableAntiSpyware.
- Double-click the value and set its data to 1.
- Click OK and restart your PC.
This will permanently disable Microsoft Defender and stop the Antimalware Service Executable from running.
Method 3: Install a Third-Party Antivirus
The safest way to disable Microsoft Defender permanently is by installing another antivirus program.
When a third-party antivirus is installed, Windows automatically disables Microsoft Defender to prevent conflicts.
This keeps your system protected while eliminating high resource usage from the Antimalware Service Executable.
Important Things to Consider
Disabling Antimalware Service Executable completely removes built-in malware protection. Without an alternative antivirus, your system becomes vulnerable to threats such as ransomware, spyware, and trojans.
If your main concern is high CPU or memory usage, consider these safer alternatives:
- Update Windows to the latest version
- Add exclusions for large folders
- Schedule scans during idle hours
- Upgrade RAM or switch to SSD
In most cases, high usage is temporary and occurs during full system scans or updates.
FAQs
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
Antimalware Service Executable is the background process of Microsoft Defender Antivirus. Its file name is MsMpEng.exe. It provides real-time protection against malware.
Why is Antimalware Service Executable using high CPU?
High CPU usage usually occurs during full system scans, background updates, or when scanning large files. It can also happen if your system has limited RAM.
Is it safe to disable Antimalware Service Executable?
It is safe only if you install another antivirus program. Otherwise, your PC will be exposed to security threats.
Does disabling Real Time Protection permanently stop it?
No. Real-time protection automatically re-enables after restarting your PC unless you disable it using Group Policy or Registry Editor.
Will installing another antivirus disable Microsoft Defender automatically?
Yes. Windows automatically disables Microsoft Defender when it detects another active antivirus program.
Can I reduce usage without disabling it?
Yes. You can schedule scans, add exclusions, and update your system to reduce resource consumption.
Ending Lines
Antimalware Service Executable plays a critical role in protecting your Windows 11 and Windows 10 system. While high CPU or memory usage can be frustrating, completely disabling Microsoft Defender should be your last option.
If performance is your concern, try adjusting scan schedules or adding exclusions before turning off protection entirely. If you decide to disable it permanently, always install a trusted antivirus solution to keep your system secure.
